


| Pair Name | Eurycomalactone, Cisplatin | ||
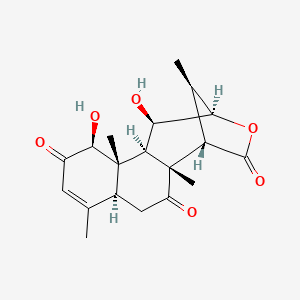
| Phytochemical Name | Eurycomalactone (PubChem CID: 441793 ) | ||
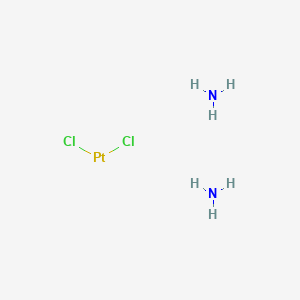
| Anticancer drug Name | Cisplatin (PubChem CID: 5702198 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Eurycomalactone, Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | NFKB1 | hsa4790 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Activity | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Result | This finding provides a rationale for the combined use of chemotherapy drugs with ECL to improve their efficacy in NSCLC treatment. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inactivation of AKT/NF‑κB signaling by eurycomalactone decreases human NSCLC cell viability and improves the chemosensitivity to cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 2020 Oct;44(4):1441-1454. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7710. | Click |
